Unraveling the Enigma: What is the Difference Between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
In the realm of vision enhancement technologies, two popular methods stand out: thermal imaging and night vision. Both offer valuable capabilities in low-light conditions, but they operate on distinct principles, bringing unique advantages and limitations. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of thermal imaging and night vision, unraveling their mysteries, and exploring how they revolutionize the way we perceive our surroundings in the dark.
Understanding Night Vision:
Night vision technology is designed to amplify existing ambient light, enabling users to see in low-light environments. This technology relies on specialized devices equipped with image intensifier tubes, which amplify the small amount of available light and convert it into visible images. While night vision can be remarkably effective in enhancing vision at night, it does have its limitations, particularly in total darkness when ambient light is scarce.
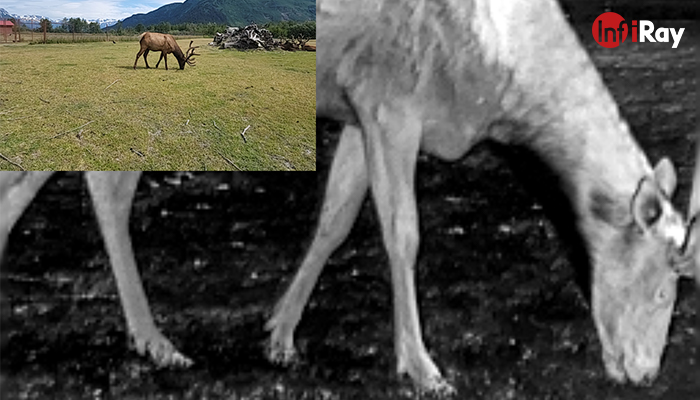

Comparison of visible light and thermal imaging of a reindeer
Decoding Thermal Imaging:
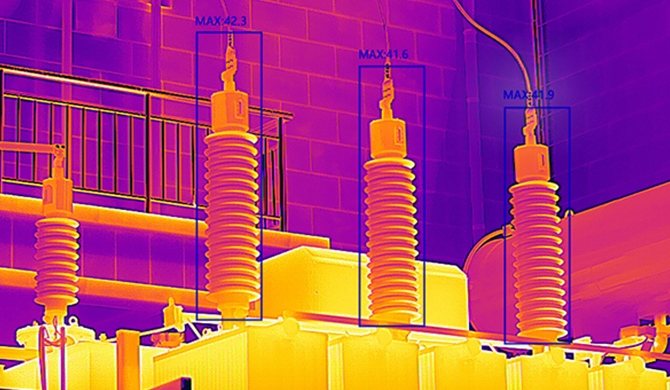
Thermal imaging operates on an entirely different principle. Rather than relying on ambient light, it detects and visualizes the heat emitted by objects and organisms. This fascinating science is based on the detection of infrared radiation, and thermal cameras are capable of capturing temperature variations in their surroundings. The advantages become most pronounced in total darkness, where its unique features offer unparalleled benefits.
Advantages of Thermal Imaging in Total Darkness:
Thermal imaging systems do not require any ambient light to operate, making them highly effective in pitch-black environments where night vision may struggle. While night vision may perform better under moonlit conditions, it remains unaffected by the absence of moonlight or artificial lighting, offering consistent performance in all lighting situations.
It excels at identifying heat signatures, making it highly effective at detecting camouflaged objects, animals, or potential intruders hidden from the naked eye. In security and surveillance applications, thermal cameras provide a reliable means of spotting suspicious activities even when traditional surveillance systems may fall short.
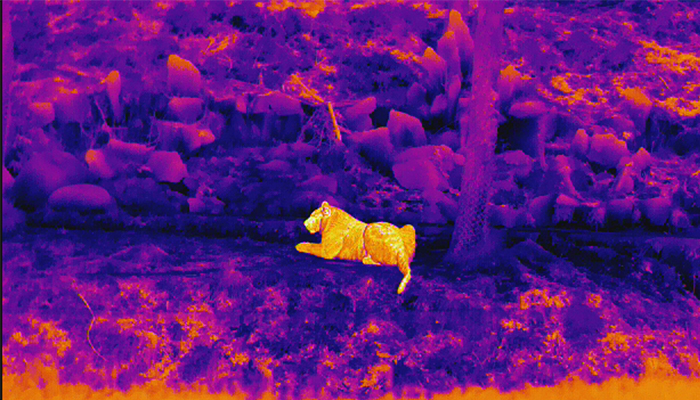

Details of the tiger in the jungle 200m away
Thermal imaging can see through smoke, fog, and dust, enabling rescuers and law enforcement personnel to navigate challenging environments more effectively. In hazardous situations, such as firefighting or search-and-rescue missions, thermal imaging enhances situational awareness, enabling responders to make more informed decisions.
Thermal imaging plays a crucial role in locating missing persons in vast, remote areas or disaster-stricken regions, even when visibility is extremely limited. In wildlife research and conservation efforts, it allows researchers to observe nocturnal animals without causing disruption to their natural behavior. Thermal cameras aid in detecting potential equipment malfunctions, electrical issues, or insulation problems in industrial settings, preventing costly breakdowns and accidents.
Night Vision's Shortcomings:
Night vision heavily relies on ambient light sources, making it less effective in total darkness. Changes in lighting conditions can impact the performance of night vision devices, leading to reduced visibility in varying environments.
Night vision struggles to identify camouflaged or concealed objects since it relies on amplifying ambient light rather than detecting heat signatures. While night vision can be effective in some security scenarios, its inability to detect hidden targets may limit its applications in certain surveillance tasks.
Night vision's reliance on ambient light can hinder its performance in environments with obstructions such as smoke and fog. In extreme or challenging conditions, night vision may suffer from reduced image clarity, potentially hindering critical operations.
Thermal imaging and night vision each offer distinctive advantages and limitations in enhancing vision in low-light conditions. While night vision relies on amplifying existing light, thermal imaging stands out for its independence from ambient light sources and the ability to detect heat signatures. The unique features of thermal imaging make it particularly advantageous in total darkness, revolutionizing applications such as security, surveillance, search and rescue, wildlife observation, and industrial inspections. As technology continues to evolve, both thermal imaging and night vision will continue to play essential roles in shaping how we perceive and interact with the world in low-light environments.
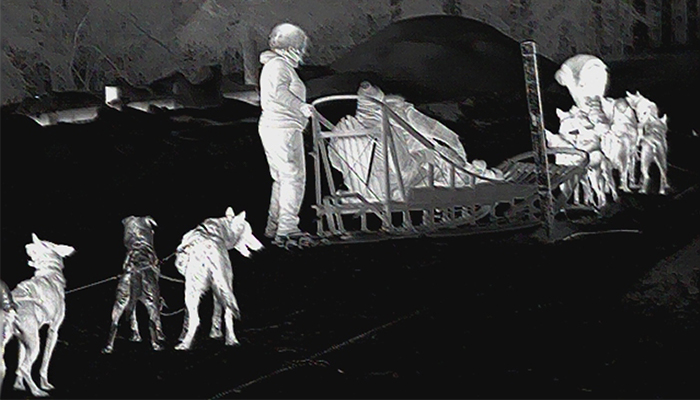

Farmers and dog in a hunting yard under thermal imaging