Quick Guide to Deep Understanding Infrared Thermography

In the modern world, technology has become a cornerstone in various industries, and one of the groundbreaking technologies making a significant impact is Infrared thermography. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep understanding of Infrared imaging tech, covering its definition, applications, advantages, and best practices. Whether you're a professional in the field or someone curious about this fascinating technology, let's delve into the intricacies of Infrared thermography.
What You'll Learn:
A. Definition of Infrared Thermography
Infrared thermography involves utilizing infrared cameras to capture the heat emitted by an object or surface. This technology translates thermal energy into visible light, enabling the observation and analysis of temperature variations.
B. Importance in Various Industries
From building inspections to medical diagnostics, infrared thermography is indispensable in detecting issues that might be invisible to the naked eye. Its non-invasive nature and ability to identify anomalies make it a valuable tool across diverse sectors.
C. Purpose of the Comprehensive Guide
This guide aims to provide a quick yet comprehensive overview, enabling readers to grasp the fundamentals of infrared thermography and its applications.
1. Basics of Infrared Thermography
1.1 How Infrared Imaging Works
Infrared cameras detect the infrared radiation emitted by objects, creating images based on temperature differences. This process enables the visualization of heat patterns, making it a powerful diagnostic tool.
1.2 Spectrum of Infrared Light
Understanding the infrared spectrum is crucial. Different objects emit varying levels of infrared radiation, and by analyzing these patterns, we gain insights into the temperature variations within a given scene.
1.3 Applications in Science and Technology
Infrared thermography finds applications in diverse fields, including scientific research and technological advancements. Its ability to capture thermal data opens doors to innovations in areas such as materials science and electronics.

2. Key Components of Infrared Thermography
2.1 Infrared Cameras
The heart of infrared thermography lies in specialized cameras designed to detect and record thermal radiation. These cameras vary in features, and choosing the right one depends on the specific application.
2.2 Image Processing Software
To make sense of the captured thermal data, image processing software is essential. This software helps in analyzing and interpreting infrared images, turning raw data into actionable insights.
2.3 Temperature Measurement Devices
Accurate temperature measurement devices complement infrared thermography, providing precise readings for comprehensive analysis. Integrating these devices enhances the reliability of thermal inspections.
3. Applications of Infrared Thermography
In the realm of infrared thermography, applications span across various industries, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in different scenarios. Understanding the diverse ways in which this technology is employed sheds light on its significance and the impact it has on enhancing safety, efficiency, and reliability.
3.1 Building Inspections: Beyond the Surface
In the domain of building inspections, infrared thermography emerges as a game-changer, delving beyond what meets the eye. It excels in identifying concealed issues such as insulation defects, water leaks, and structural anomalies. By capturing thermal images, it provides a non-invasive means of assessing the condition of buildings, allowing for early intervention and preventive maintenance. This ensures not only structural integrity but also contributes to energy efficiency, a crucial factor in sustainable construction practices.
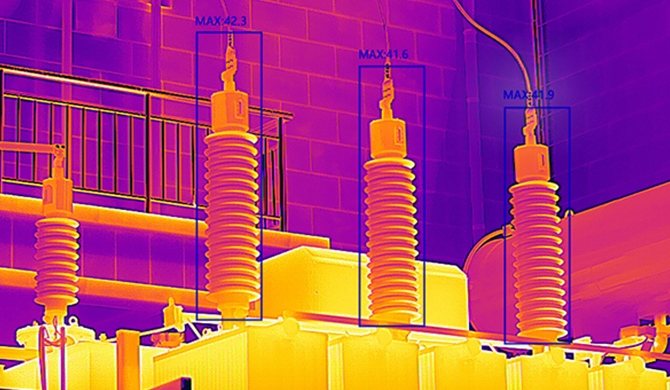
3.2 Electrical Systems: Unveiling Hidden Threats
Electrical inspections harness the power of infrared thermography to reveal hidden threats within complex systems. Overloaded circuits, faulty connections, and potential fire hazards often manifest as temperature variations. Infrared cameras excel in pinpointing these issues, enabling prompt corrective measures. This proactive approach not only prevents catastrophic failures but also extends the lifespan of electrical components, ensuring the safety and reliability of critical systems.
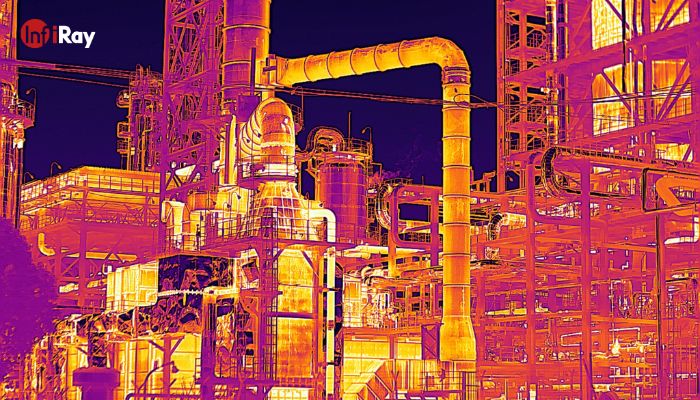
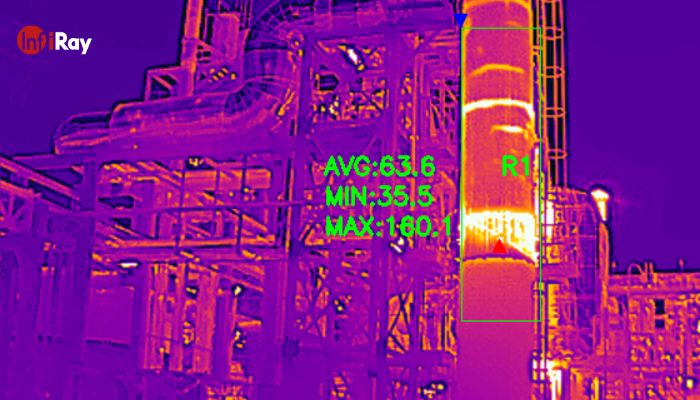
3.3 Industrial Equipment Maintenance: Predictive Precision
In the realm of industrial equipment maintenance, infrared thermography serves as a predictive maintenance tool, offering precision in identifying potential failures before they occur. By detecting overheating components in machinery, it allows for timely intervention, reducing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency. The ability to schedule maintenance based on actual conditions, rather than fixed intervals, enhances cost-effectiveness and minimizes disruptions to production processes.
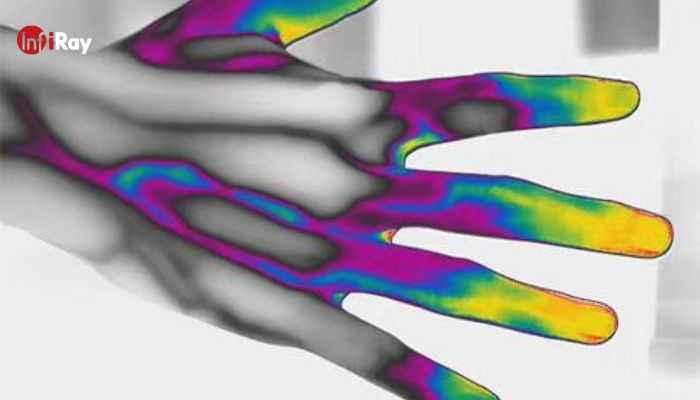
3.4 Medical Diagnostics: Non-Invasive Insights
In the field of medical diagnostics, infrared thermography provides non-invasive insights into the human body's thermal patterns. By detecting abnormal temperature variations, it aids in the early diagnosis of conditions such as inflammation or circulatory disorders. This technology offers a valuable alternative to traditional diagnostic methods, providing a holistic view of health conditions without the need for invasive procedures.

3.5 Environmental Monitoring: Beyond the Human Eye
Beyond traditional applications, Infrared thermography finds a niche in environmental monitoring. It allows for the assessment of environmental conditions, including the detection of heat anomalies in ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and even the monitoring of climate change effects. This extension of its applications underscores the technology's adaptability and relevance in addressing contemporary environmental challenges.

4. Advantages and Limitations
4.1 Benefits of Infrared Thermography
• Non-invasive and non-contact inspection method
• Early detection of potential issues
• Time and cost-effective compared to traditional methods
• Applicable in various environmental conditions
4.2 Limitations and Considerations
• Accuracy dependent on equipment quality
• Limited penetration in certain materials
• Interpretation skills crucial for accurate analysis
• Adverse weather conditions may affect the results

However, with ongoing technological advancements, state-of-the-art infrared cameras now possess the capability to conquer challenging weather conditions, including rain, snow, and harsh environments. This breakthrough ensures improved visibility in adverse weather, making these high-end devices invaluable for applications like outdoor surveillance and industrial inspections. The resilience of modern infrared cameras extends to harsh environments, showcasing their robust performance in extreme temperatures and rugged conditions. This technological progress not only enhances practical applications but also underscores the evolving landscape of infrared thermography.

5. Best Practices for Effective Infrared Inspections
5.1 Proper Equipment Handling
Understanding the capabilities of your infrared camera and ensuring proper calibration is fundamental for accurate results. Regular maintenance and calibration checks enhance the reliability of the equipment.
5.2 Environmental Conditions
Conducting infrared inspections in suitable environmental conditions is essential. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and air movement can impact the accuracy of thermal readings.
5.3 Interpretation of Infrared Images
Skillful interpretation of infrared images is crucial. Training and experience play a significant role in identifying anomalies and making informed decisions based on thermal data.
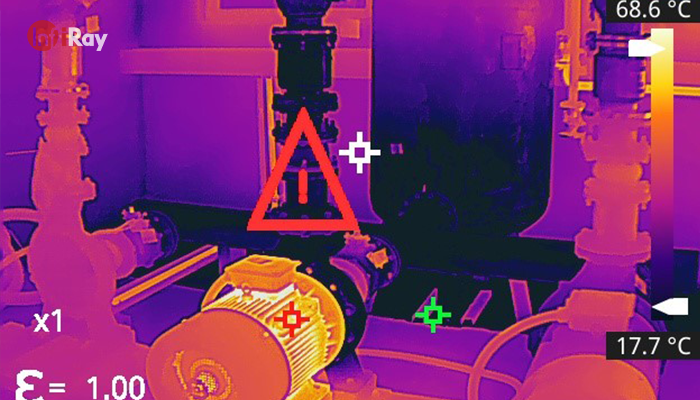

6. Future Trends in Infrared Thermography
6.1 Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development in infrared thermography lead to continuous advancements in camera technology, image processing algorithms, and data interpretation tools. The future holds the promise of even more sophisticated and accurate thermal inspections.
6.2 Emerging Applications
As technology evolves, new applications for infrared thermography are likely to emerge. From space exploration to environmental monitoring, the versatility of this technology opens doors to exciting possibilities.
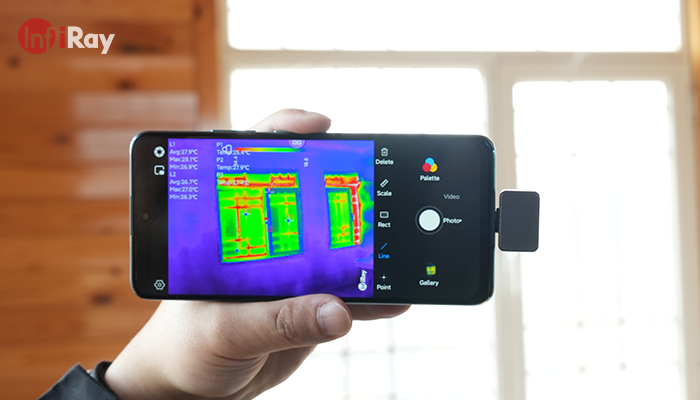

Infrared thermography is a powerful technology with applications ranging from building inspections to medical diagnostics. Understanding its basics, key components, applications, and best practices is essential for harnessing its full potential. As technology advances, Infrared thermography continues to play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of various systems. Stay curious, explore new applications, and embrace the possibilities that this cutting-edge technology offers.