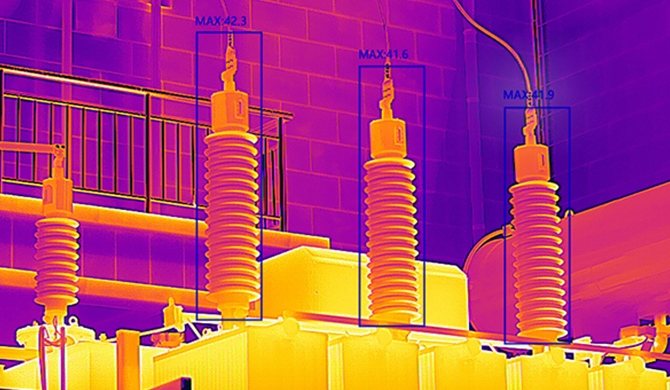
Thermal Camera 101: An Essential Primer

In today's technologically advanced world, where innovation is at the forefront of various industries, thermal cameras have emerged as powerful tools with a wide range of applications. From industrial processes to security and healthcare, thermal imaging cameras offer invaluable insights by capturing and visualizing infrared radiation, which is emitted by objects based on their temperature.
Introduction to Thermal Cameras
Thermal cameras, also known as infrared cameras or thermographic cameras, are devices designed to detect and display temperature variations in objects. Unlike conventional cameras that capture visible light, thermal imaging cameras work by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects. This radiation is converted into a visible image, commonly referred to as a thermal image or thermogram, which represents the temperature distribution across the scene.
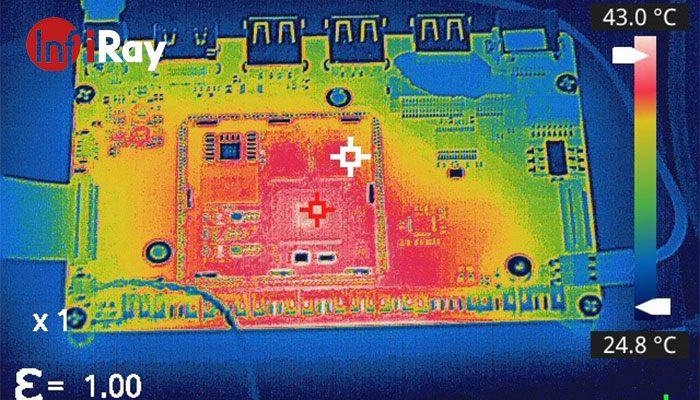

How Thermal Cameras Work
At the heart of a thermal camera lies its sensor, which is sensitive to infrared radiation. The sensor captures the infrared radiation emitted by objects and converts it into electrical signals. These signals are then processed to create a visual representation of the temperature distribution. The resulting image assigns different colors or shades to varying temperatures, allowing users to identify hotspots and temperature differences quickly.
Applications of Thermal Cameras
Thermal imaging cameras find applications across a diverse range of industries:
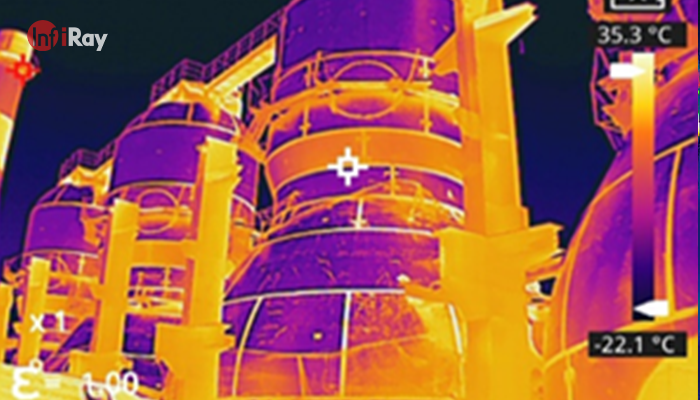
1. Industrial and Manufacturing:
· Predictive Maintenance: Detecting overheating components to prevent equipment failures.
· Quality Control: Identifying defects in manufactured products by analyzing temperature variations.
· Process Monitoring: Ensuring consistency and efficiency in industrial processes by monitoring temperature changes.

2. Security and Surveillance:
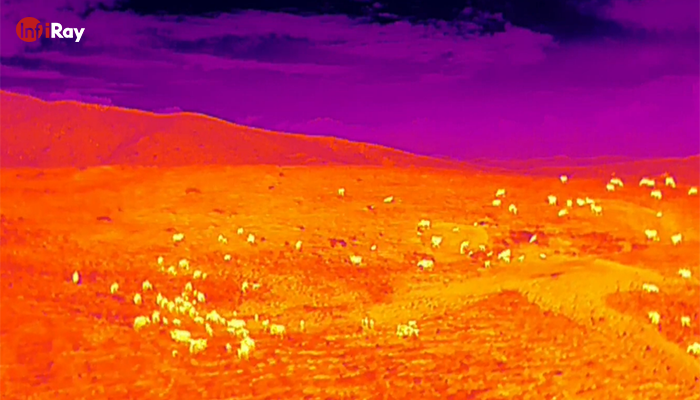
· Intrusion Detection: Noticing human or animal intrusions in restricted areas, even in complete darkness.
· Perimeter Monitoring: Monitoring large areas for any unusual temperature changes that could indicate potential threats.
· Night Vision: Providing clear visibility in low-light conditions.

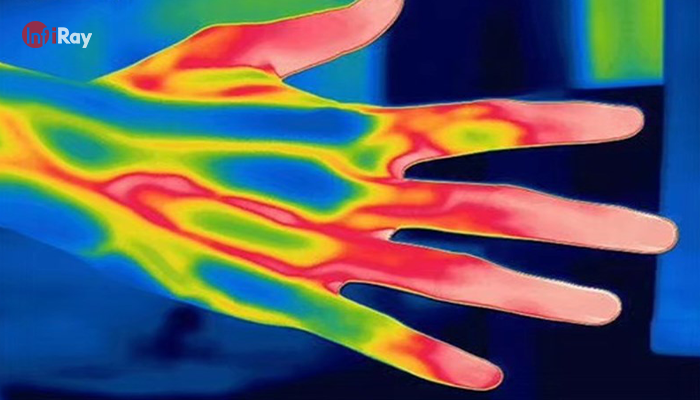
3. Medical and Healthcare:
· Fever Detection: Screening individuals for elevated body temperatures, often used for rapid health assessments.
· Thermography in Diagnostics: Identifying anomalies in blood circulation and identifying inflammation in medical examinations.
4. Firefighting and Search & Rescue:
· Identifying Hotspots: Pinpointing areas with high heat intensity during firefighting operations.
· Locating Survivors: Searching for survivors in disaster-stricken areas based on temperature differences.
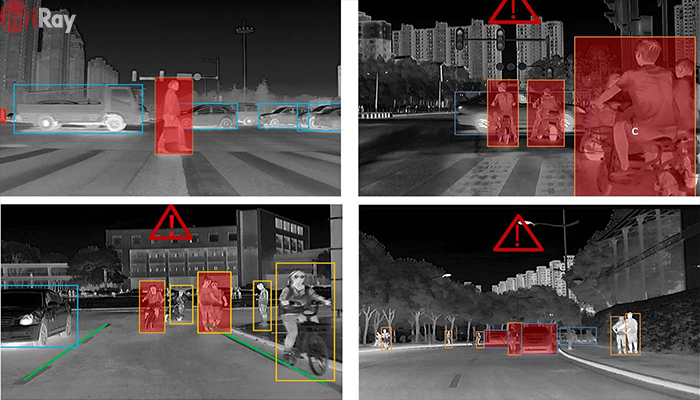
5. Automotive:
· Driver Assistance Systems: Enhancing driving safety by detecting pedestrians and obstacles even in low visibility conditions.
· Enhanced Vision: Providing drivers with a clearer view of the road and surroundings.

6. Building and Home Inspection:
· Energy Efficiency Assessment: Identifying areas of heat loss in buildings for improved energy efficiency.
· Structural Anomalies Detection: Locating leaks, insulation issues, and other structural problems.
Types of Thermal Cameras
There are different types of thermal cameras available in the market, including uncooled and cooled infrared cameras, handheld and fixed installations, and infrared cameras versus thermal imagers. Each type has its advantages and limitations, catering to specific needs and applications.
Factors Influencing Thermal Camera Performance
Several factors affect the performance of thermal imaging, including the temperature range they can detect, sensitivity, resolution, frame rate, and environmental conditions like humidity and atmospheric interference.
Practical Considerations
Proper use and handling of thermal cameras are crucial for accurate results. Regular calibration and maintenance ensure consistent performance over time. However, it's important to note that thermal imaging cameras do have limitations. For instance, they cannot see through glass or certain materials and may have difficulties distinguishing objects with similar temperatures.
Selecting the Right Thermal Camera
Choosing the right thermal imaging camera requires identifying your specific needs, considering your budget, researching different brands and models, and reading user reviews and expert opinions. A well-informed decision will lead to a more effective investment in the long run.
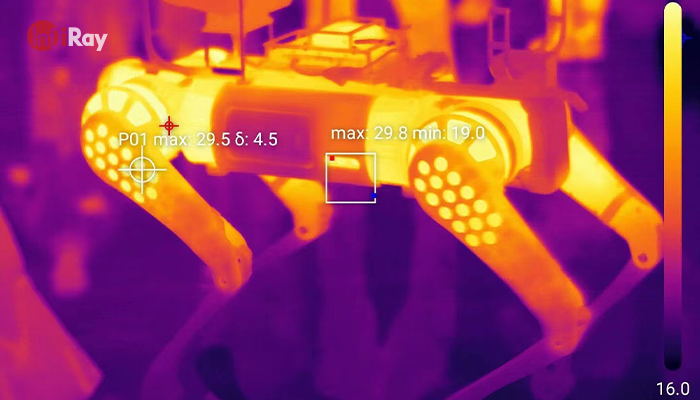

Future Trends in Thermal Imaging
As technology advances, thermal imaging cameras are likely to benefit from improved sensor technology, integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning, increased portability, and the exploration of new applications.
Thermal cameras have transcended their initial use in military and industrial applications to become indispensable tools across various sectors. Their ability to capture temperature differences and provide valuable insights has revolutionized industries and improved safety and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, the future of thermal imaging holds even more exciting possibilities.