6 Top Uses of Infrared Thermal Cameras for Cement Industries

In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, cement plants are witnessing significant growth in production scale and value. However, the complexity of production processes and equipment poses numerous safety hazards. Traditional inspection methods often fall short in terms of real-time monitoring and accuracy, making it challenging to meet modern safety standards. Here's where infrared thermal cameras step in, offering non-contact temperature measurement, precise monitoring, and efficient inspection capabilities, providing robust safety measures for cement plant operations.
Background
With rapid industrialization, cement plants are expanding both in scale and value. However, the intricate production processes and equipment make them susceptible to various safety hazards. Traditional inspection methods struggle to provide real-time and accurate monitoring, failing to meet modern safety standards. InfiRay infrared thermal cameras, with their wide temperature range and high precision, are emerging as crucial tools for safety monitoring in cement plants.
6 Top Uses of Infrared Thermal Cameras for Cement Industries
1. Coal Bunker Safety Monitoring
Coal, with its natural tendency to self-ignite, poses a significant risk of spontaneous combustion in coal bunkers. Traditional manual inspection methods often fail to provide real-time and accurate temperature monitoring, leading to inaccurate identification of ignition points. Moreover, harmful gases produced during coal oxidation pose risks to inspection personnel. Infrared thermal cameras enable real-time monitoring of coal pile temperature distribution, accurately identifying potential ignition areas, and triggering cooling measures promptly, thus preventing fires and ensuring bunker safety.
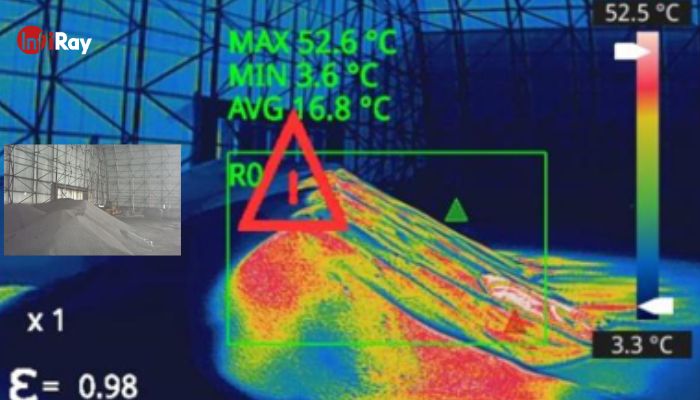
2. Conveyor Belt Operation Monitoring
Conveyor belts play a crucial role in material transportation, but prolonged operation in harsh environments can lead to belt damage. Traditional manual inspection methods are insufficient, often compromising worker safety and providing subjective results. Infrared thermal cameras enable real-time monitoring of belt temperature distribution, detecting abnormal heating caused by aging, misalignment, or material impact. They can also trigger alarms and emergency stop procedures, preventing accidents such as major belt breakage or longitudinal tearing, ensuring the safe and stable operation of production systems.
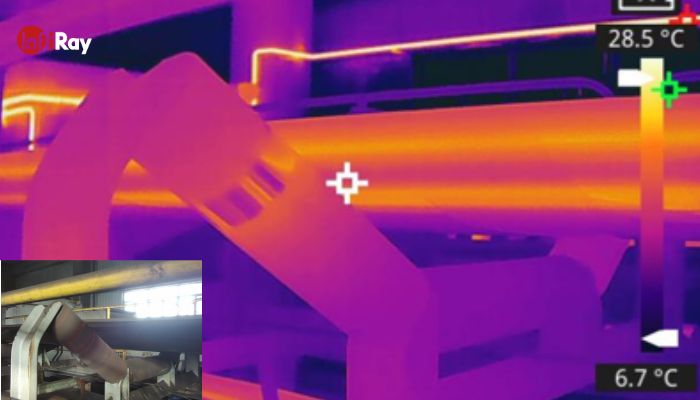

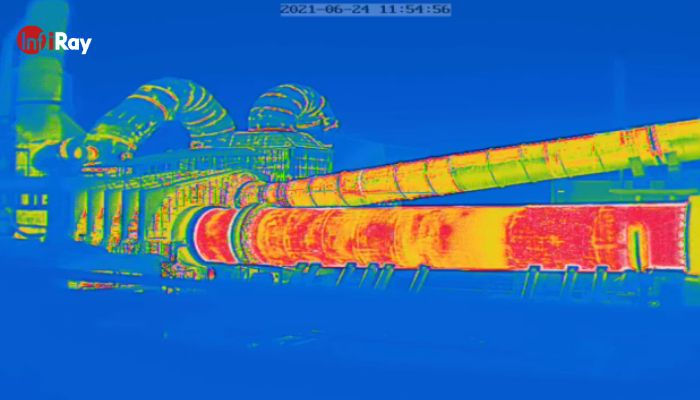
3. Cement Rotary Kiln Monitoring
Cement rotary kilns, essential equipment in cement clinker production lines, face risks of refractory material erosion and thinning during prolonged continuous operation. This erosion can lead to kiln wall burn-through, causing production shutdown accidents. Infrared thermal cameras enable remote and real-time monitoring of kiln wall temperature distribution, allowing early detection of refractory material erosion and precise localization. This information guides adjustments to combustion and shutdown maintenance, improving production efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and pollution.
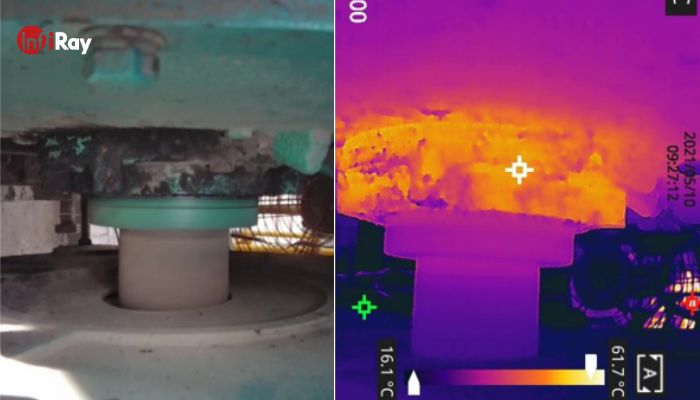
4. Motor Fault Detection
Motors are critical machinery in cement plants, and their stable operation is vital for production. Motor faults typically manifest as temperature increases. Infrared thermal cameras enable quick detection and analysis of various motor thermal faults, such as loose connections, oxidized terminals, cable overheating due to unbalanced voltage or overload, aging cores, and poor heat dissipation leading to excessive shell temperatures or uneven distribution. Operations personnel can pinpoint specific fault locations based on infrared images, facilitating timely maintenance and repair.
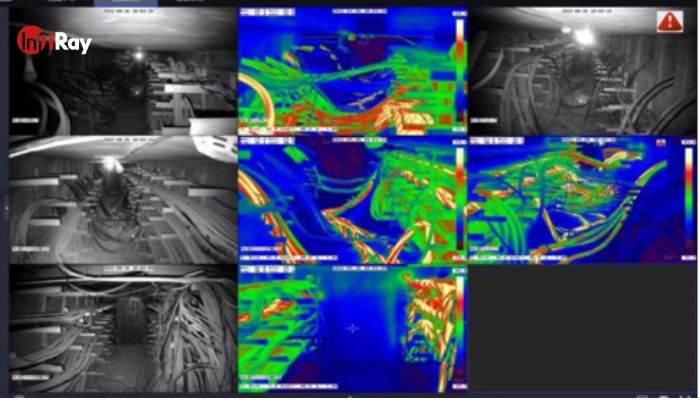
5. Cable Trench Safety Monitoring
Long-term operation of cables can lead to oxidation and heating, posing fire hazards. However, traditional manual inspection methods are inadequate due to confined spaces. InfiRay online thermal cameras collect video and temperature information from cable trenches, transmitting them to the control room in real-time. Personnel in the control room can monitor cable temperature changes, with the system issuing alarms promptly in case of anomalies, ensuring timely response and minimizing risks.
6. Critical Cabinet Temperature Monitoring
Equipment cabinets such as high and low-voltage distribution cabinets, switch cabinets, relay cabinets, and control cabinets often face internal high-temperature hazards due to their complexity and confined spaces, potentially leading to fires and production disruptions. In such scenarios, compact and convenient card-type infrared thermal cameras provide real-time monitoring of internal equipment temperatures, along with defect diagnosis and alarm outputs, ensuring the safe and stable operation of equipment inside the cabinets.
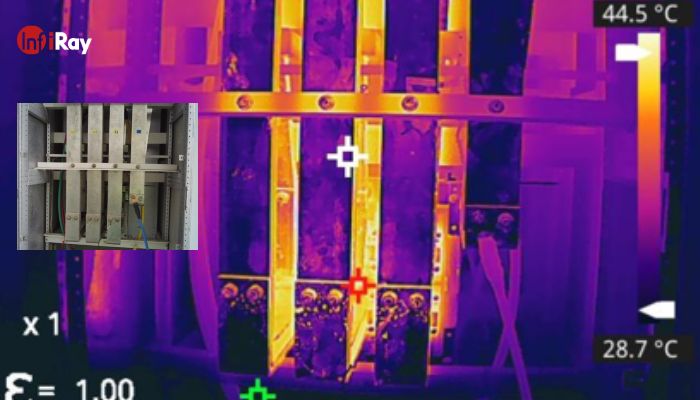
Infrared thermal cameras have revolutionized safety monitoring in cement industries, offering unparalleled capabilities in temperature monitoring and fault detection. From preventing fires in coal bunkers to ensuring the stable operation of critical equipment, these cameras play a pivotal role in enhancing safety, efficiency, and productivity in cement plants.

 français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español
Español  italiano
italiano  português
português  العربية
العربية  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  magyar
magyar 









